Alzheimer's disease is a condition that destroys the connections between cells in the brain over time. Eventually these cells die. This affects how the brain works. As cells die, the brain shrinks.
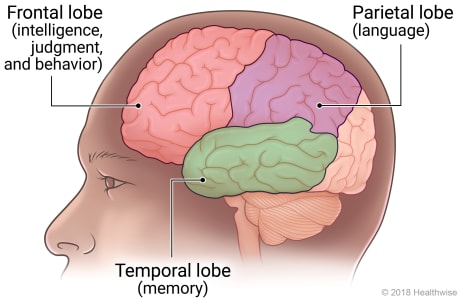
The damaged areas of the brain include the hippocampus, which is an area of the brain that helps new memories form. Damage to the frontal lobe of the brain eventually causes problems with intelligence, judgment, and behavior. Damage to the temporal lobe affects memory. And damage to the parietal lobe affects language.
Alzheimer's is the most common form of mental decline, or dementia, in older adults.
Current as of: October 1, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 1, 2025