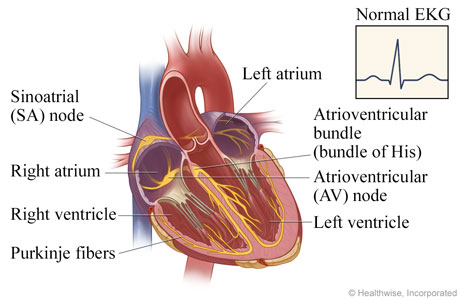
In the normal heart, electrical impulses pace the rhythm at which the heart contracts and relaxes. The sinoatrial (SA) node triggers the electrical impulse, causing the upper chambers (atria) to contract. The signal travels through the atrioventricular (AV) node to the atrioventricular bundle, which divides into the Purkinje fibers. The fibers carry the signal and cause the lower chambers (ventricles) to contract.
The electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) tracing above reflects this normal electrical activity.
Current as of: October 2, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 2, 2025